The study of landforms is a significant aspect of geomorphology. It involves examining and evaluating various features of the earth’s surface, like mountains, valleys, rivers, plains, plateaus etc, and understand how they were formed and how they have continued to evolve over time. There are several methods and approaches to study the geomorphology;
Field Work:
Fieldwork is the most common method to study the geomorphology of a particular area, which involves visiting and examining land forms in person to collect data and make observations.

The fieldwork can include taking measurements, collecting samples, and using specialized equipment to record topographical data. Fieldwork is an essential component of many studies of landforms, as it allows researchers to gather primary information about the features they are studying. Fieldwork is more important than the rest of the methods for enhancing personal learning, getting experience, developing practical skills, and fostering a deeper understanding of the landforms. It allows the fieldworkers to connect the existing theory with real-world applications, encouraging active learning and promoting the development of essential skills.
Remote Sensing:
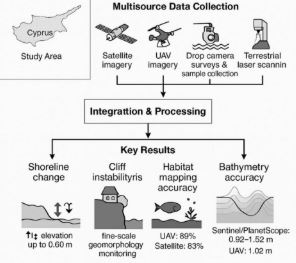
Remote Sensing is a modern technique which replaced the method of field work. It involves using satellite or aerial images to study landforms from a distance. This can provide the researchers with a bird’s eye view of the landscape, allowing them to study features that may be difficult or impossible to access on foot. Remote sensing can also be used to create maps and models of landforms, which can be used to better understand their characteristics and behavior.
Remote sensing offers significant advantages over traditional fieldwork in many scenarios, making it a preferred approach for gathering data about the Earth’s surface.
- Remote sensing can gather data from large areas, including those difficult or dangerous for human access, like mountainous terrain, dense forests, or disaster zones.
- Collecting data from vast regions through fieldwork can be expensive due to personnel, logistics, and time. Remote sensing, particularly satellite and drone-based systems, reduces these costs by minimizing fieldwork and automating data collection and processing.
- Remote sensing tools can cover large areas in a fraction of the time it would take for traditional surveying methods.
- Remote sensing offers a comprehensive overview of an area, allowing the detection of larger-scale trends and patterns that might be missed with localized fieldwork.
- Satellite imagery enables monitoring of land use, vegetation, and water bodies over time, providing valuable information on environmental changes and aiding in long-term studies.
- Remote sensing facilitates gathering vast amounts of data quickly, allowing for scalability in meeting the challenges of biodiversity conservation.
- Remote sensing can be used to identify areas of interest before deploying fieldwork teams, optimizing their efforts by directing them to areas with higher potential for investigation.
Geomorphology:

Geomorphology is the study of landforms that, how they are formed. It is an interdisciplinary field that combines geology, geography, and other sciences to study the physical processes that shape the earth’s surface. Geomorphologists use a variety of tools and techniques, including fieldwork and remote sensing, to study landforms and their evolution over time.
Geographic Information System:
Geographic Information System is a computer-based tool that allows researchers to create and analyse maps and spatial data. It can be used to study lanforms, by creating digital models of the landscape and analyzing patterns and relationships between different features. GIS can also be used to predict how lanforms may change over time, bsed on factors such as climate, erosion, and human activity.
Simulation Modeling:
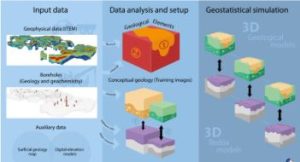
Simulation modeling is a technique that involves using computer models to simulate the behavior of landforms over time. This can be used to perdict how lanforms may evolve in response to different factors, such as climate change or human activity. Simulation modeling can be powerful tool for understanding the complex interactions between different physical processes that shape lanforms.
You may like to read:
- Realms of Physical Environment
- Erosional Features of the Groundwater
- Work of Sea (Erosion by sea)/ Coastal Erosion
- Erosion carried out by Glaciers (Work of Glaciers)
Hey there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help
from an established blog. Is it very difficult to
set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things
out pretty fast. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any
points or suggestions? Thanks