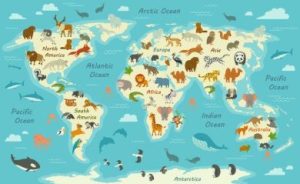
What is Biogeography
Biogeography Biogeography is a fundamental branch of Physical Geography, and a fundamental field in Biology as well. It deals with the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in…
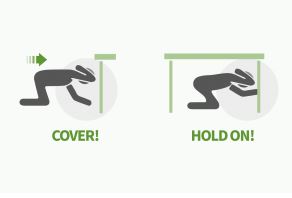
How to protect during an Earthquake ?
How to protect during an earthquake? It is not the Earthquakes that cause casualties and fatalities, but rather the man-made structures, which do not withstand Earthquakes. During an earthquake, the…
EarthQuakes | A detailed description of the Earthquakes.
What is an Earthquake? An Earthquake is a sudden trembling and shaking of Earth’s surface caused by the release of a huge amount of energy in lithosphere (crust+solid mantle). The…
Types of geomorphology
Although historical and process studies are dominant over modern geomorphological enquiry, particularly in English-speaking nations, however, other types of study also exist. For example, structural geomorphologists, who were once very…
Pacific Ring of Fire
What is The Ring of Fire? The ring of fire, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, The Rim of Fire, The Circum-Pacific Belt, or The Girdle of Fire,…
Trends and Development in Geomorphology
Trends in Geomorphology Geomorphology is a fundamental branch of physical geography which helps us study landforms and the processes that shape them. Over the years, several trends in the field…
Methods and approaches to geomorphological study
The study of landforms is a significant aspect of geomorphology. It involves examining and evaluating various features of the earth’s surface, like mountains, valleys, rivers, plains, plateaus etc, and understand…
Realms of Physical Environment
The physical environment of our earth can be divided into four realms; 01. The solid part is known as the Lithosphere. 02. The liquid part is known as the Hydrosphere.…
Erosional Features of the Groundwater
What is Groundwater? All water occuring beneath the ground surface is called “groundwater”. It has been estimated that the volume of water in the upper 0.8 kilometer of the continental…
Work of Sea (Erosion by sea)/ Coastal Erosion
Work of Sea Sea Coast: The land and sea meeting place is called the “coast”. Sea coasts may have many kinds of shapes. The chief types of sea coasts are…