Depending upon their mode of formation, the soil deposits have been broadly grouped into two classes: (i) residual soil deposits, and (ii) transported soil deposits. What are different types of Soils?
Residual Soil Deposits

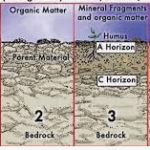
In plain areas, the products of rock weathering continue to accumulate in places over the parent rock masses and give rise to a “residual soil deposit”. As the action of weathering decreases with depth, such soil deposits gradually change from soil at the surface to broken rock fragments and merge with fresh rock underneath. The common examples of residual soil are laterite, terra rosa, and peat bogs.
Transported Soil Deposits

The weathered and broken rock materials are eroded and transported from one place to another by natural agencies, such as wind, water, ice, or gravity. The deposits of soil formed in this manner are called “transported soil deposits”. Such soils generally have no relation with underlying rock mass. The transported soils have been classified according to the nature of the transporting agency responsible for their formation. This classification has been given in the following lines;
- Soil transported by rivers is known as “Alluvial Deposits”.
- Soil transported by lakes is known as “Lacustrine Deposits”.
- Soil transported by the movement of seawater is known as “Marine Deposits”.
- Soil transported by wind is known as “Eolian Deposits”.
- Soil transported by glacial movement is known as “Glacial Deposits”.
The size of soil particles is extremely variable. It ranges from a big boulder to fine clays. As per the international standard the nomenclature of soil particles according to their sizes is as under;
- Soil containing a mixture of clay and sand is called “Loam”.
- The clayey soil that appreciably has a sufficient amount of lime is known as “marl”.
- If the size of soil particles is 60mm or more, it is known as “Boulder”.
- If the size of soil particles is between 2.0 and 60 mm, it is known as “Gravel”.
- If the size of soil particle is between 0.6 and 2.0 mm, it is known as “Coarse Sand”.
- If the size of soil particles is between 0.2 and 0.6, it is known as “Medium Sized Sand”.
- If the size of soil particles is between 0.06 and 0.2, it is known as “Fine Sand”.
- If the size of soil particles is between 0.002 and 0.06, it is known as “Silt”.
- If the size of soil particles is less than 0.002, it is known as “Clay”.
to be continued………… coming soon
Posts you may like :

Leave a Reply